GUI编程
1、简介
GUI的核心技术: Swing AWT,界面不美观
不流行的原因:
- 因为界面不美观
- 需要JRE环境
为什么我们要学习?
- 可以写出自己心中想要的小工具
- 工作时候也可能维护swing界面
- 了解MVC架构,了解监听
2、AWT
2.1、AWT介绍
- 包含了很多类和接口!GUI!
- 元素:窗口,按钮,文本窗
- java.awt
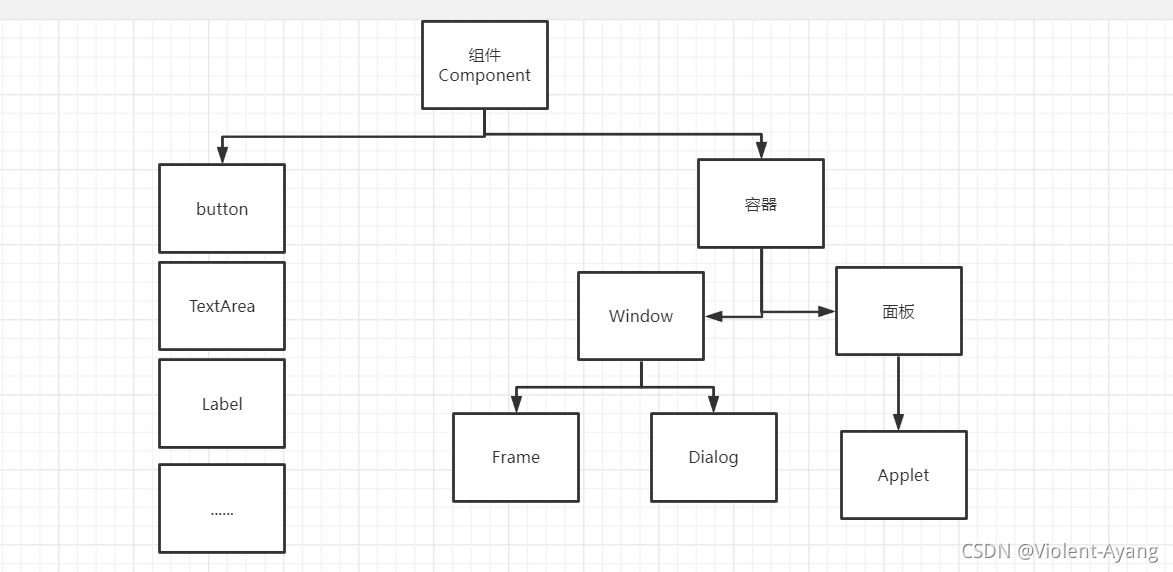
2.2、组件和容器
1.Frame
1 | package GUI.lesson1; |
回顾封装:
1 | package GUI.lesson1; |
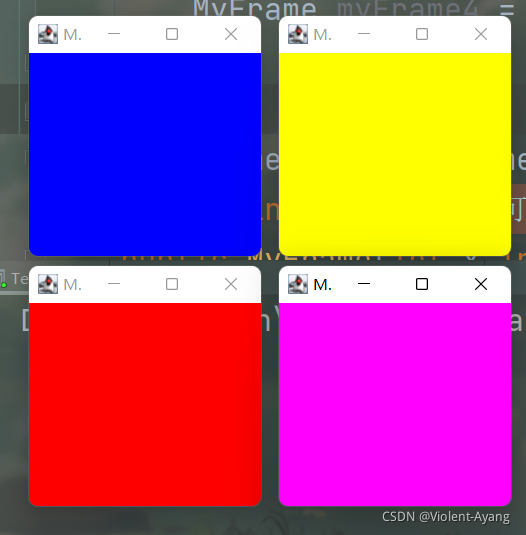
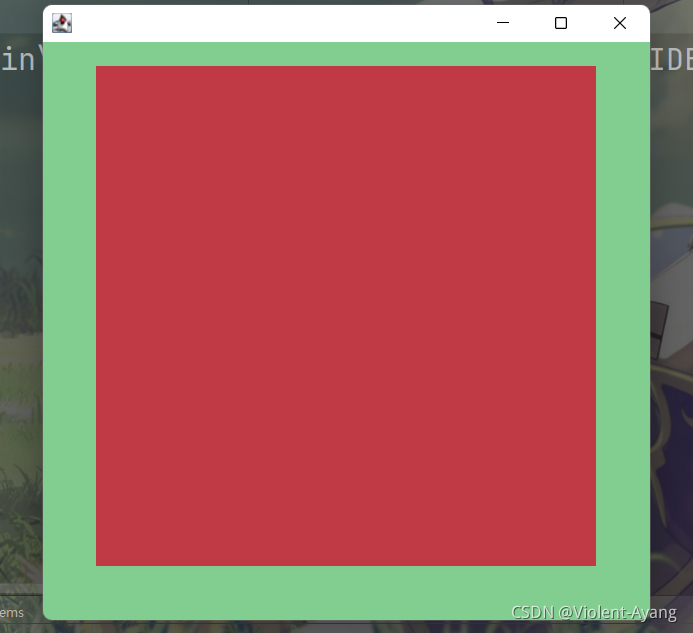
2.面板Panel
解决了关闭事件
1 | package GUI.lesson1; |
2.3、布局管理器
- 流式布局
1 | package GUI.lesson1; |
- 东西南北中
1 | package GUI.lesson1; |
- 表格布局
1 | package GUI.lesson1; |
练习
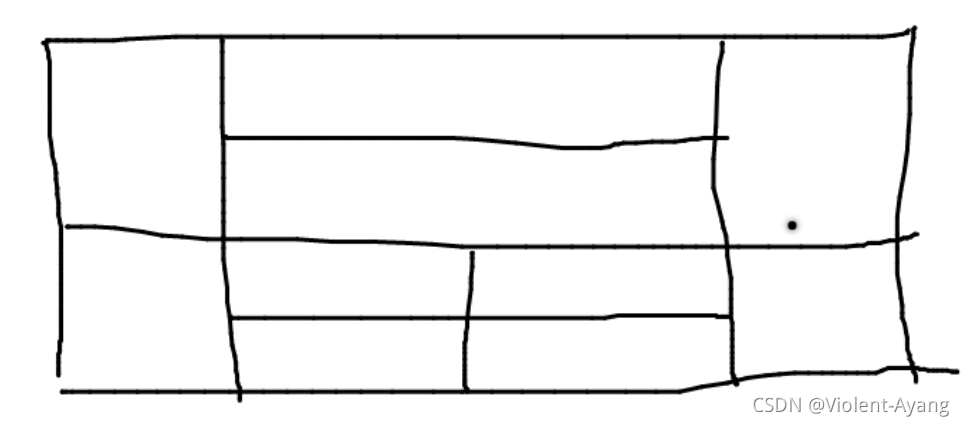
在每块空格处加上按钮
1 | package GUI.lesson1; |
总结:
- 1.Frame是一个顶级窗口
- 2.Panel 无法单独显示,必须添加到某个容器中
- 3.布局管理器
1.流式布局
2.东西南北中
3.表格布局
2.4、事件监听
事件监听:当某个事情发生的时候,干什么?
1 | package GUI.lesson2; |
多个按钮共享一个事件
1 | package GUI.lesson2; |
2.5、输入框TextField
1 | package GUI.lesson2; |
2.6、简易计算器,组合内部类回顾复习
目前代码
1 | package GUI.lesson2; |